
|
|||
|
CASE REPORT / CAS CLINIQUE
HYDROCEPHALUS: A RARE PRESENTATION OF CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TOXOPLASMOSIS IN THE ACQUIRED IMMUNODEFICIENCY SYNDROME
HYDROCEPHALIE: UN CAS RARE DE TOXOPLAMOSE CEREBRALE DANS LE CADRE D'UN SYNDROME D'IMMUNO-DEFICIENCE ACQUISE
E-Mail Contact - DJIENTCHEU Vincent de Paul :
vincent_djientcheu@yahoo.com
SUMMARY The incidence of HIV infection and the neurological complications are increasing, especially in developing countries. Hydrocephalus due to cerebral toxoplasmosis is very rare and only 7 cases have been reported in the literature . The authors report a case of hydrocephalus related to toxoplasmosis of the 4th ventricles in a HIV patient successfully treated medically without shunting. The mechanism of the hydrocephalus is a necrotizing ependymitis and plexitis obstructing the CSF flow although the cerebral parenchyma has a normal CT appearance in many cases. CNS toxoplasmosis should be ruled out in any immuno-deficient patient with hydrocephalus of unknown origin. The permanent CSF shunting may not be necessary in hydrocephalus due to CNS toxoplasmosis, and external CSF shunting may only rarely be needed. Keywords : CNS toxoplasmosis, AIDS, hydrocephalus, medical treatment, Cameroon RESUME Les auteurs présentent un cas d’hydrocéphalie associée à une toxoplasmose du IV ème ventricule chez un patient HIV positif, traité médicalement avec succès, sans dérivation du LCS. Le mécanisme de l’hydrocéphalie est une épendymite et une plexite nécrosante obstruant la circulation du LCS, même si le parenchyme cérébral apparaît normal au scanner dans plusieurs cas. Une toxoplasmose du système nerveux central doit être recherchée chez tout patient immunodéprimé avec une hydrocéphalie d’étiologie indéterminée. Une dérivation permanente du LCS ne serait pas nécessaire au cours de l’hydrocéphalie entrant dans ce cadre. La dérivation ventriculaire externe peut être implantée dans de rares conditions. Mots clés: Afrique, Cameroun, Hydrocéphalie, Toxoplasmose, VIH, SIDA INTRODUCTION Toxoplasmosis is the most common infection of the central nervous system in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (7, 11). The classic presentation is that of a single or multiple focal lesions with mass effect. Sometimes it may present as diffuse encephalitis. The authors report a case of hydrocephalus related to toxoplasmosis in an AIDS patient successfully treated with anti-toxoplasma drugs without shunting. CASE REPORT A 41 year-old man presented in our General Medicine Service on July 7, 2001 with headaches, dizziness, gait disorders since one week and a 3 months history of weight loss and intermittent chronic diarrhea. The physical examination on admission revealed a cerebellar syndrome with ataxia, broad-based gait, dysarthria and nystagmus. The cerebral CT scan (figure 1) showed hydrocephalus with dilatation of both lateral, third and fourth ventricles. After intravenous administration of contrast material, there was enhancement of the ependymal and the subependymal tissue of the wall of the 4th ventricle and the distal portion of the aqueduct of Sylvius (figure 2). The density of the fluid in the 4th ventricle was slightly higher than that measured in the 3rd ventricle and the ependymal canal of the spinal cord. The HIV serum assay (ELISA) was positive for HIV1 antibodies. The toxoplasma serology (ELISA) was positive for IgG (titre = 69) and was negative for IgM (result obtained later after the patient was already discharged). T Lymphocyte CD4 count was 60/mm3. DISCUSSION The incidence of hydrocephalus due to tuberculous meningitis, cryptococcal meningitis or the so-called «low pressure hydrocephalic state in the absence of an active infection» in AIDS patients may be on the increase in developing countries, undoubtedly related to the high spread of the virus and the inaccessibility to anti-retroviral therapies (7, 8, 14). The challenge of the neurosurgeon in this context is to carefully select the candidate that will need CSF shunting, given the high cost of the valve and the prognosis of the underlying disease. Hydrocephalus due to cerebral toxoplasmosis is a very rare condition with only 7 cases reported in the literature (2, 5, 6, 9, 13, 14). The present patient makes the 8th case reported. The usual presentation of cerebral toxoplasmosis is a single or multiple focal lesions (necrotizing abscesses) with mass effect and surrounding oedema; it may also present as diffuse encephalitis (7,10). The mechanism of hydrocephalus in 2 of the previously reported cases (9, 13) is a compression of the CSF pathway by surrounding parenchymatous space-occupying lesions (necrotizing abscesses). In the 5 other cases (2, 5, 6, 14), hydrocephalus was due to a blockage of the CSF-flow within the ventricular system and the ependymal canal by an exudate from a necrotizing ependymitis and plexitis. On Computerized Tomography scan, the exudate is hypodense and corresponds on post-mortem examination (2, 5, 6, 14) to an eosinophilic gelatinous material infiltrated by inflammatory cells (macrophages, lymphocytes, microglia and a few granulocytes). The exudate contains numeous cysts and tachyzoite forms of Toxoplasma. The density of this exudate obstructing the CSF-flow is similar to the density of CSF on CT-scan imaging, suggesting an unimpaired passage of CSF within the ventricular system as observed in a communicating hydrocephalus. Apart from the ependymal and the subependymal lesions, the rest of the cerebral parenchyma has a normal CT appearance, although some micro-abscesses are discovered on post-mortem examination (5, 6, 14). The mechanism of hydrocephalus in the authors’ case may be similar to that of the 5 last reported cases (2, 5, 6, 14) and corresponds to a necrotizing ependymitis and plexitis of the 4th ventricle. This feature of the so-called «necrotizing ependymitis and plexitis» on a contrast CT is not described in the previously reported cases (only non-contrast CT scans were performed). In the present case, there was an ependymal and subependymal contrast enhancement in the aqueduct and the 4th ventricle wall, dilated by a CSF- like fluid (probably the reported eosinophilic gelatinous exudate). The density of this fluid was slightly higher than that of CSF, probably due to the protein content, giving the impression of a cystic dilatation of the 4th ventricle. The diagnosis of cerebral toxoplasmosis is a combination of clinical, radiological, biological and parasitological arguments, but the favourable course of a cerebral mass lesion on antitoxoplasma medication in an AIDS patient is the more clinically useful test (10). The identification of the parasite in the CSF sample is uncertain even in patent cases of CNS toxoplasmosis (2). Antitoxoplasmic antibody assays lack specificity and sensitivity (2, 6, 7, 9, 10). This may be due to the immunodepression and the particularity of the immune system of the central nervous system where serology for local infections such as neurocysticercosis can be positive in the CSF but negative in the peripheral blood even in immunocompetent patients. In areas of high prevalence of HIV infection and poverty, any AIDS patient developing focal neurological signs should be treated as cerebral toxoplasmosis and the CT scan should be performed only in patients who do not show clinical improvement (10). The gold standard management of post meningitis hydrocephalus is not well known in AIDS patients. To date, few data are available on the role of CSF shunting in hydrocephalus due to AIDS. Nadvi and colleagues (15) in a series of 30 patients with post-tuberculous hydrocephalus did not find any improvement by the CSF shunting in the HIV positive group compared with the HIV negative group. No patients with tuberculous meningitis grade 3 and 4 survived in the HIV positive group (15). Other authors have also found this correlation between the outcome and the grade at initial presentation (1, 3, 12, 16). Considering the cost of this surgery, Nadvi and collaborators suggest that HIV positive patients with tuberculous meningitis may undergo an external CSF drainage and only those who present a significant improvement may be considered for shunt surgery irrespectively of the CD4 count (15). Walter’s experience is successful in shunting some patients with post-cryptococcal meningitis and he also proposed the external CSF drainage for the selection of good candidates for the internal CSF shunting (16). The association of Toxoplasmosis and hydrocephalus is a very rare condition reported in AIDS. Many cases may be under diagnosed or missed. In the previous reported cases, patients died despite a CSF external drainage (2, 5, 6, 9, 13, 14). Medical treatment was not associated to the surgery and the diagnosis of CNS toxoplasmosis was done on post-mortem examination. The favorable course of the present case on medical treatment demonstrates the important role of anti-toxoplasma medication in the management of this complication, besides shunt surgery. The progression of the infection to the brain stem may be responsible for brain death. A permanent CSF-shunting may not be necessary and the external CSF drainage may be rarely needed in hydrocephalus due to toxoplasmosis. CONCLUSION CNS toxoplasmosis should be ruled out in any immunodeficient patient with hydrocephalus, even when the cerebral parenchyma has a normal CT appearance. The effective diagnostic tool in such a situation is a therapeutic trial with antitoxoplasma medication. The identification of the parasite in the CSF is uncertain and the antitoxoplasma serology lacks sensitivity and specificity. A permanent internal CSF shunt may not be necessary in these patients and external CSF drainage, beside the medical treatment may be needed only rarely. 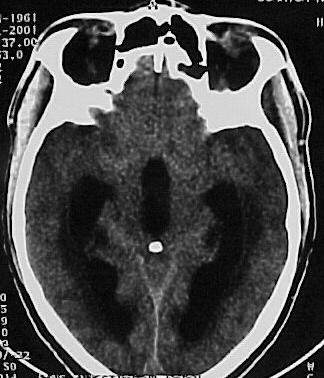 Figure 1 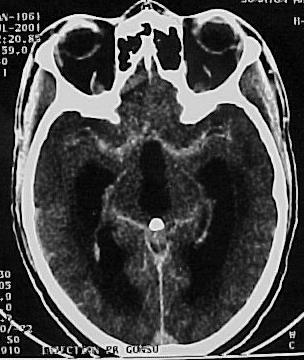 Figure 2
REFERENCES
|
© 2002-2018 African Journal of Neurological Sciences.
All rights reserved. Terms of use.
Tous droits réservés. Termes d'Utilisation.
ISSN: 1992-2647